Some of the most common skin conditions are caused by infections and others are a consequence of genetic factors combined with environmental factors. In this article, we give you some examples of skin diseases caused by different factors, describing their symptoms, treatments and how to prevent them.
Skin and dermatology
To better understand the characteristics of the skin, we recommend reading previous articles such as rare skin diseases and their relationship with genetics or basic care for sensitive skin. In them, we explain in detail, among other things, that the skin is the largest organ of the human body, and that it is made up of three layers: the epidermis, the dermis, and the hypodermis. The skin performs several functions, among which we can highlight its role as a protective barrier that defends our body from the aggressions of external agents such as viruses and bacteria, among others.
This protective capacity can be altered if an element inflames or irritates the skin. The discipline that is in charge of studying, preventing and treating the various pathologies that affect the skin, as well as the care of healthy skin, is called dermatology. These pathologies that affect the skin can range from primary skin diseases to systemic diseases whose symptoms are manifested through the skin. Most skin diseases are not serious, however, they usually carry annoying symptoms that can also influence the patient’s mood, since most of them are usually visible.
7 common skin diseases and their origin
The origin of skin diseases can be very diverse. As we have mentioned before, some are the consequence of fungal or viral infections, while other environmental and genetic factors intervene or may even be caused by immunological problems.
Below, we are going to look at some of the most common skin diseases, including one whose cases have increased worryingly in recent years: melanoma, which is a type of skin cancer.
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is characterized by the appearance of white spots of different sizes on different parts of the body, mainly in those most exposed to the sun, such as hands, arms, face, and feet. The spots have well-defined edges and sometimes they have a darker or reddish appearance. Also, vitiligo usually leads to the early appearance of gray hair, especially in the areas of the spots.
The disease occurs as a consequence of the destruction or malfunction of the melanocytes, which are the cells that produce melanin (a pigment that determines the color of hair and skin). Therefore, although it affects all skin types, it is more noticeable in dark skin tones.
It is not a contagious disease or with a serious prognosis, however, it can cause sunburn or skin cancer among other complications. Vitiligo-affected skin rarely regains its color, and most of the time, the lack of pigmentation spreads to various parts of the body.
Once vitiligo has been diagnosed, through blood tests or biopsy, treatments can be started to balance skin tone, such as:
Depigmentation of unaffected areas.
Medications with corticosteroid creams.
Activation of melanocytes by exposure to UVA rays.
Surgery.
The cause of the disease is still unknown, although much research indicates that the combination of the genetic and environmental components may be responsible.
Specifically, research indicates that vitiligo has a polygenic inheritance pattern, that is, multiple alleles contribute to the genetic risk of the disease.
The relationship between genetics and the development of vitiligo has long been suspected since first-degree relatives of people with this disease have a higher incidence of vitiligo than the general population. Specifically, siblings of affected people have a prevalence of 6%, which increases to 23% in the case of twins.
Regarding environmental factors, it has been observed that exposure to various chemical substances, such as phenolic compounds, alter melanin synthesis and therefore can trigger vitiligo.
Acne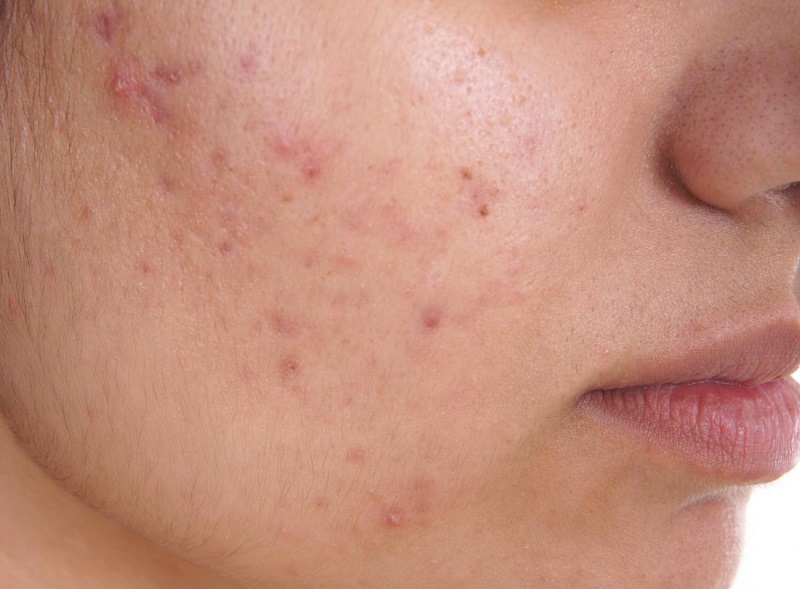
Among skin diseases, acne is the most common and best known. It has a prevalence of 80% in people between 11 and 30 years old, although its maximum incidence peak is reached in women between 14 and 17 years old and in men between 16 and 19.
In general, acne, in any of its degrees, usually remits spontaneously between 20-25 years. Although some women suffer from it beyond 40.
The disease is characterized by the appearance, usually on the face, of comedones (pimples with sebum) that can break and become infected, becoming pustules or even forming cysts.
Acne occurs because the hair follicles become clogged with dead skin cells, bacteria, or dry sebum that builds up and blocks the sebum that should come to the surface of the skin through the pores.
Depending on the damage done to the skin, and the number of pimples present, acne can be mild, moderate or severe.
It is a multifactorial disease, that is, it is caused by the intervention of several factors, which in this case are genetic, environmental and individual to the skin.
Studies have recently shown the heritability of acne. Recent research from King’s College Institute of Dermatology and geneticists from the same university found 15 acne-related genetic variants that influenced the shape of hair follicles, making them more likely to develop bacterial inflammation.
The trigger for acne is usually puberty, a stage in which a hormonal change occurs, especially an increase in androgens, and this causes stimulation of the sebaceous glands.
Although it usually disappears spontaneously, a dermatologist can recommend treatments focused on relieving the signs of acne in each case.
Skin cancer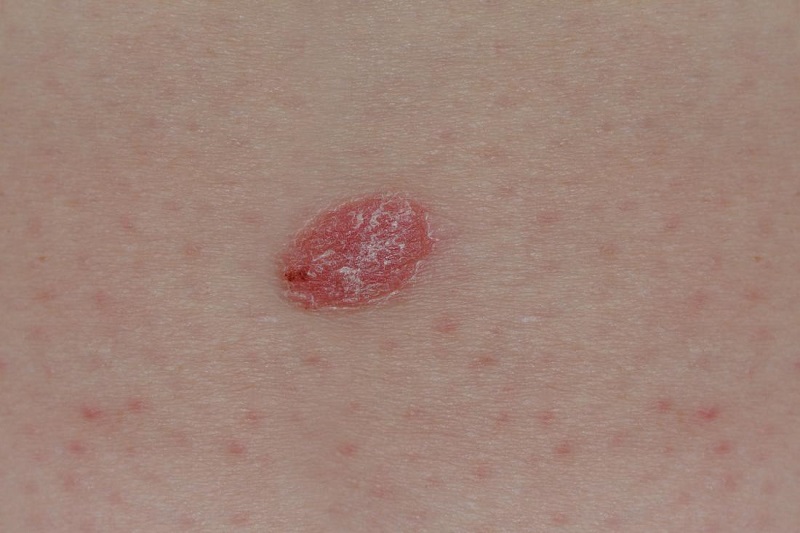
This type of cancer arises when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably. Due to damage to their DNA caused mainly by ultraviolet radiation.
Although it is more frequent in areas of the body exposed to the sun such as face, neck, chest, arms, and legs. It can also occur in areas that are not normally exposed. Such as the palms of the hands or under the nails.
Among the types of skin cancer that exist, melanoma is the most dangerous. Since in its advanced stage it can spread to internal organs and therefore put the person’s life at risk.
Detected in time, it usually has a cure, so we must pay close attention to its first manifestations, which include:
Large brownish spots with smaller dark specks.
Moles that change the size, color, or bleed.
Small lesions with irregular edges and parts in a reddish, white or bluish color.
Lesions accompanied by itching or burning.
Dark lesions on the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, or mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, vagina, or anus.
The number of melanoma cases has tripled in the past 20 years. The proliferation of outdoor activities or tanning salons is some of the reasons that are considered to explain this great increase.
The main treatment for this type of skin cancer is surgery to remove malignant growth. If the cancer is advanced, treatment with chemotherapy, radiation therapy. Or immunotherapy is done to slow the progression of the disease.
Genetic and environmental factors intervene in the development of this disease. In about 10% of cases, melanoma occurs in several members of the same family. These family cases are usually due to hereditary genetic changes that increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. Today, several genes associated with melanoma are known, although the most studied are CDKN2A and MC1R.
As for the environmental factors, highlights the intense exposure to the sun. For this reason, we must become aware of the importance of using protection, especially on the face. Every month of the year, as we explained in the post. The importance of using facial sun cream all year round.
Athlete’s foot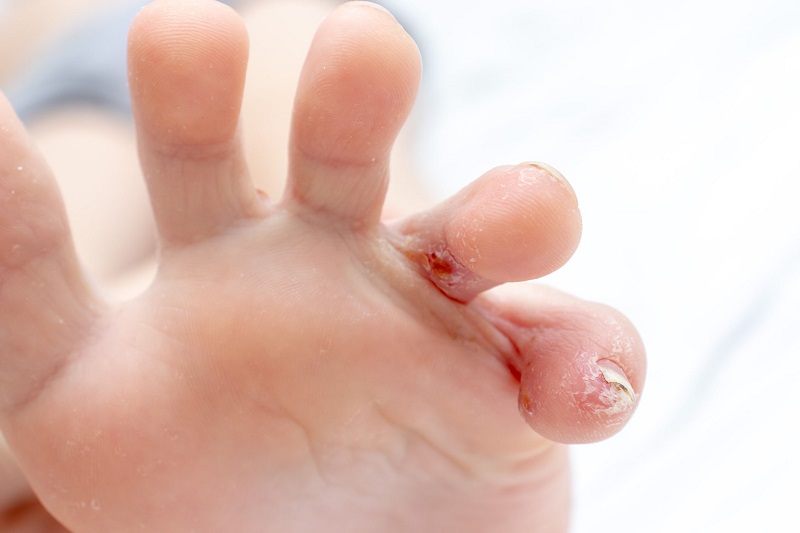
This skin disease is an infection caused by a fungus, and it usually begins between the toes. The disease is characterized by rashes that can be accompanied by itching and burning and that can cause scaling.
Finfoot is very contagious, as it can easily spread to other parts of the body of the affected person. Or other people by having contact with the infected part or sharing, for example, a towel.
The fungus that causes fin foot is the same fungus that causes ringworm. It is a microorganism whose growth is favored in humid and warm environments. That is why some practices that increase the risk of contracting this skin disease are:
Regularly wear wet or very tight socks and shoes.
Sharing footwear, bedding, or mats with someone who has the infection.
Go barefoot in public places favorable to the development of the fungus. Such as saunas, changing rooms, swimming pools or common showers.
The finfoot is treated with antifungal creams, which destroy the fungus.
Warts
Warts are benign epidermal prominences that can appear anywhere on the body. Although they are more frequent on the fingers and hands.
They are usually asymptomatic, although sometimes they can cause mild pain, and although they usually disappear on their own after a couple of years, they can also be eliminated earlier by treatments such as the application of drugs with salicylic acid or cryotherapy, which consists of in applying liquid nitrogen to the wart, among others.
Warts are caused by some types of human papillomavirus, of which there are at least 150 variants.
Viruses that cause warts can be spread by skin contact or by sharing objects.
Because it is an infection, each person’s immune system responds differently. And young children or those who are weakened by diseases such as AIDS or transplants are more vulnerable.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is caused by an acceleration of the life cycle of skin cells, which causes them to accumulate on the surface of the skin leading to reddish scales and spots that cause itching and even pain.
Symptoms vary from person to person, but the most common are:
Red spots on the skin covered with scales.
Dry and cracked skin that can even bleed.
Itching, burning, and pain.
Nails thicker than normal and cracked.
Swollen joints.
Psoriasis manifests itself in outbreaks, which can last for weeks or months. And then diminish, although they reappear after time since it is a chronic disease that has no cure. Therefore, the control of symptoms is the main objective of the treatments, which can be of three types:
Topical: creams, usually with corticosteroids that are applied in mild cases of psoriasis.
Phototherapy: it is based on radiation with ultraviolet light, either natural or artificial.
Systemic medications, such as retinoids: used in more severe cases of psoriasis or when it is resistant to other treatments.
Psoriasis is multifactorial since both genetic and environmental factors are involved.
Having parents with psoriasis has been shown to increase the risk of getting this same disease. In a meta-analysis comparing genetic variations in 39,000 participants, 16 markers associated with psoriasis were identified.
Among the environmental factors that increase the chances of suffering from psoriasis, we find a weakened immune system, high levels of stress, obesity or smoking.
As you can see, many skin diseases, including melanoma, are associated with a genetic risk. Advances in genetic research in this type of pathology will allow the development of personalized medicine, leading to more accurate diagnostic methods and treatments. From Veritas, as always, we encourage you to have a proactive attitude in your health care, to achieve complete well-being and try to prevent these and other pathologies. With our genetic tests, you can know your genetic information and act accordingly to have a higher quality and longer life.
You may also like to read- https://whizowl.co.uk/
